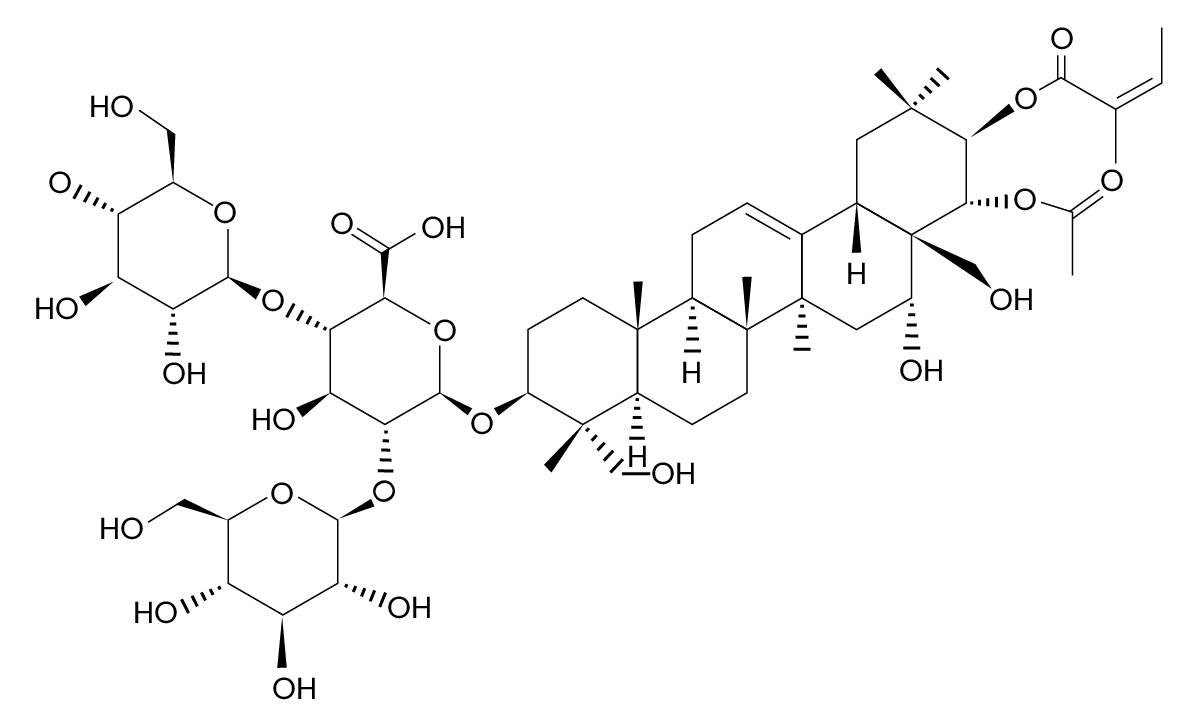
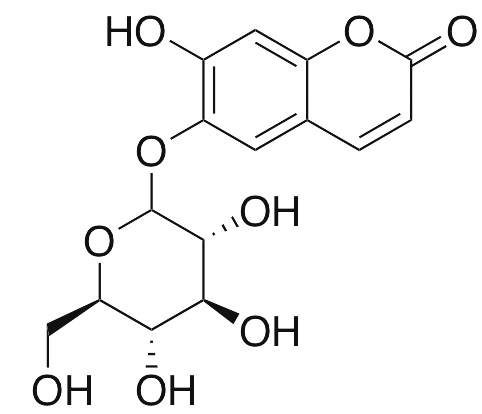
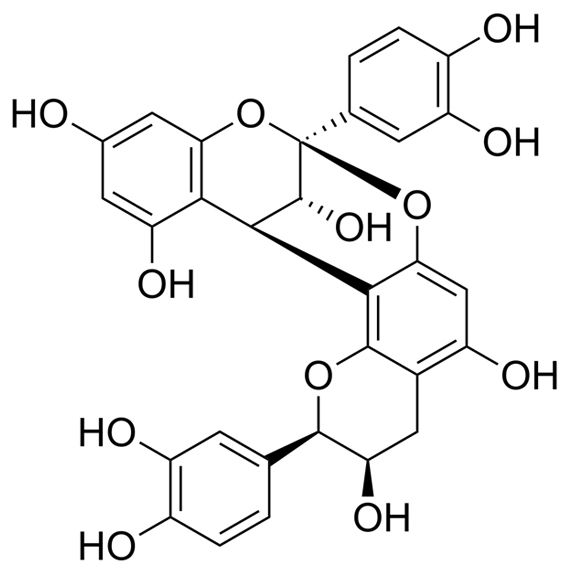
The horse chestnut seeds are rich in saponins (3–5%) out of which thirty molecules are isolated and characterized. The principal biologically active component of horse chestnut seed extract is escin, mixture of acylated triterpene glycosides composed of crypto-, α- and β-escin. The two major glycosides in the escin mixture contain the aglycone protoescigenin, glucuronic acid, and two glucose molecules. The two aglycones differ only at the C-21 position (R) which is acylated by either angelic acid or tigilic acid. Along with escin, other compounds such as proanthocyanidin A2 and esculin were also reported (Fig. 1).
Escin, a key component found in certain supplements, is recognized for its potential to support vascular health and maintain normal circulatory function. Its properties may contribute to the overall wellness of the vascular system. Additionally, proanthocyanidin A2, when used in dietary supplements, is explored for its role in supporting the body’s natural process of skin health and regeneration. Esculin is valued for its potential to support healthy microcirculation, contributing to the maintenance of normal blood flow. These compounds are known for their potential roles in supporting the body’s natural mechanisms for maintaining health.”